In Brazil, waste biomass pyrolysis equipment has emerged as a promising solution to tackle two pressing issues: waste management and energy generation. Waste biomass pyrolysis involves heating organic waste materials in the absence of oxygen to produce biochar, a soil amendment, and bio-oil, a liquid fuel that can be used to generate electricity. The equipment used for this process has the potential to significantly reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, while also providing a renewable source of energy.
The Brazilian government has been promoting the use of waste biomass pyrolysis equipment (qué significa carbonización) as part of its efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increase the share of renewable energy in the country’s energy mix. In 2020, Brazil was the ninth largest emitter of greenhouse gases in the world, with the majority of emissions coming from deforestation, agriculture, and energy production. Waste biomass pyrolysis equipment can help reduce emissions by diverting organic waste from landfills, which are a major source of methane emissions, and by providing a renewable source of energy that can replace fossil fuels.
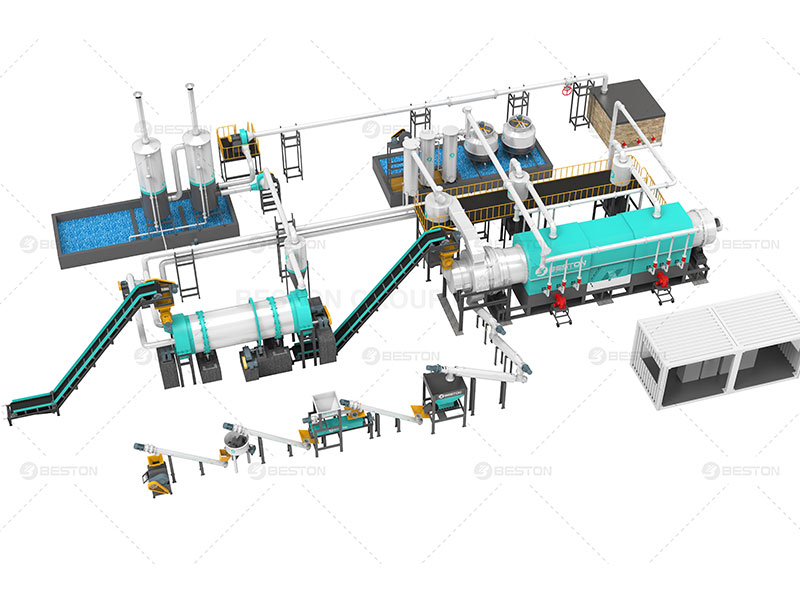
There are several companies (servicio de Beston Group) in Brazil that manufacture waste biomass pyrolysis equipment, ranging from small-scale systems suitable for household use to larger systems that can process several tons of waste per day. One example is the company Ecomaster, which produces pyrolysis equipment for both residential and commercial use. Ecomaster’s equipment can process a wide range of organic waste materials, including food waste, garden waste, and even animal carcasses.
Another company that produces waste biomass pyrolysis equipment is Enersoltec, which specializes in large-scale systems for industrial use. Enersoltec’s equipment can process up to 10 tons of waste per day and produces bio-oil that can be used as a substitute for diesel fuel. The company has implemented its technology in several projects across Brazil, including a waste-to-energy plant in São Paulo that processes organic waste from the city’s markets and generates electricity for the local grid.
Despite the potential benefits of waste biomass pyrolysis equipment (Máquina para Hacer Carbón de Cáscara de Café), there are several challenges that need to be addressed for the technology to be more widely adopted in Brazil. One of the main challenges is the lack of infrastructure for collecting and transporting organic waste from households and businesses to pyrolysis facilities. In many cities, waste management is still done through traditional collection methods, such as curbside pickup, which can make it difficult to separate organic waste from other types of waste.
Another challenge is the cost of the equipment, which can be prohibitively expensive for small-scale users. While the cost of waste biomass pyrolysis equipment has been decreasing in recent years, it is still higher than other waste management solutions, such as composting or anaerobic digestion. This makes it difficult for households and small businesses to justify the investment in the technology, especially in low-income areas where waste management is already a challenge.
In conclusion, waste biomass pyrolysis equipment (https://www.bestoneco.com/maquina-para-hacer-carbon-vegetal-en-brasil/) has the potential to be a game-changer in Brazil’s waste management and energy sectors. By diverting organic waste from landfills and producing renewable energy, it can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a more sustainable future. However, in order for the technology to be more widely adopted, there needs to be a greater investment in infrastructure and a reduction in the cost of the equipment. With the right policies and incentives, waste biomass pyrolysis equipment could become a key component of Brazil’s transition to a low-carbon economy.